Purpose
As industries increasingly adopt automation, it's important to distinguish between traditional robots and collaborative robots (cobots). This article provides a clear comparison to help you understand their capabilities, limitations, and ideal use cases.
Definitions
- Robot: A programmable machine capable of performing tasks autonomously, typically in isolated environments for safety and speed.
- Cobot: A collaborative robot designed to work safely alongside humans, often requiring minimal safety barriers.
Robot vs Cobot: Core Differences
| Feature | Robot | Cobot |
|---|---|---|
| Safety | Requires fencing, limited human interaction | Built-in safety sensors, safe to work near humans |
| Programming | Complex, requires engineers | Often no-code or low-code, user-friendly |
| Flexibility | Optimized for repetitive, high-speed tasks | More adaptable for mixed tasks and workflows |
| Cost | High upfront cost and maintenance | Lower total cost of ownership |
--- Use Cases ---

Industrial Robot in Automotive Assembly
Robots are widely used in automotive manufacturing for welding, painting, and repetitive assembly operations that require speed and precision.
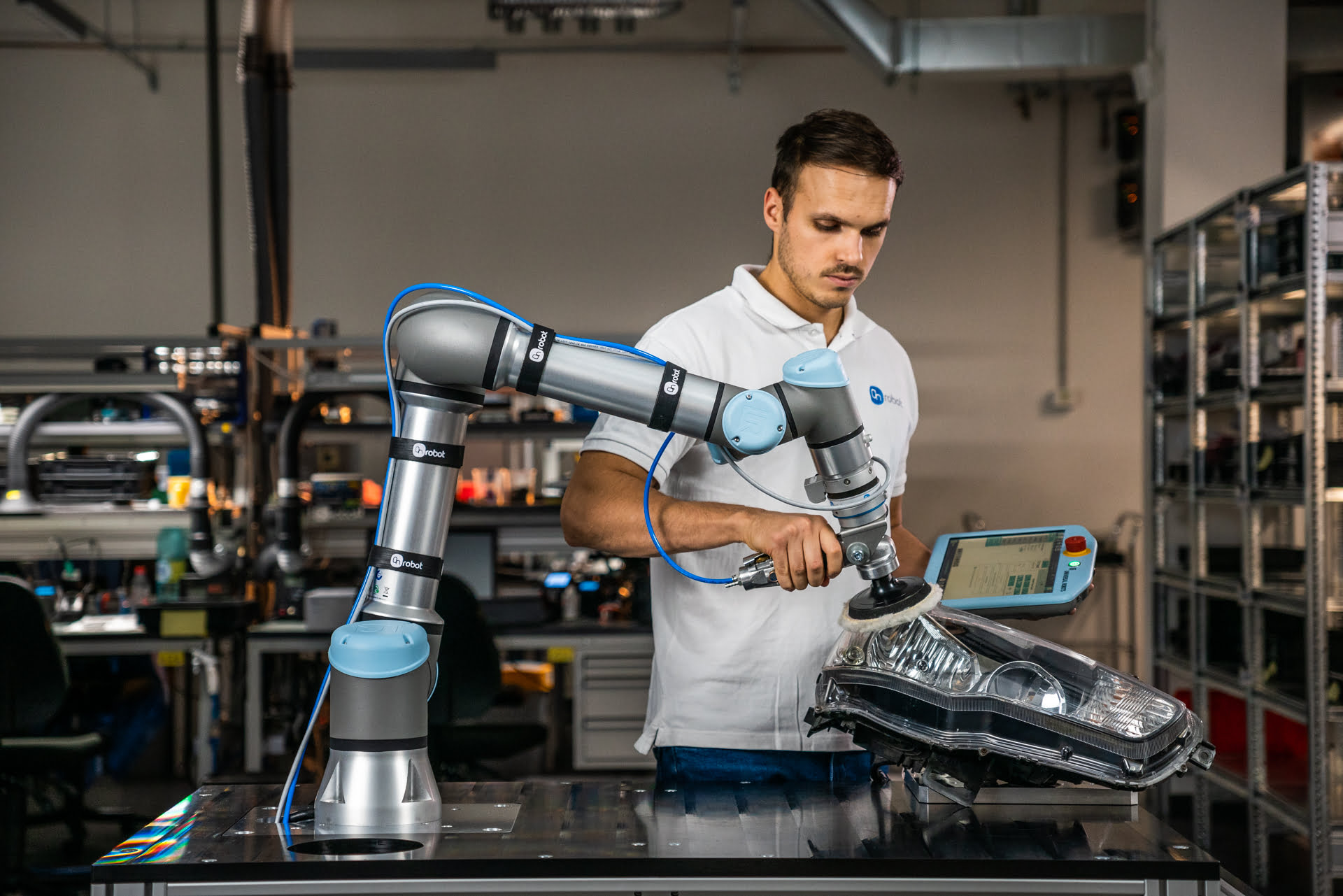

Cobot Assisting in Electronics Testing
Cobots are used in small-batch assembly, packaging, quality inspection, and tasks where humans and machines collaborate in shared spaces.
Benefits of Cobots
- Rapid deployment and programming
- Smaller footprint in factories
- Increased safety and flexibility
- Quick ROI for small and medium enterprises (SMEs)
Challenges in Adoption
Both robots and cobots present challenges depending on the environment and purpose:
- Robots: Require substantial investment, complex setup, and can displace workers.
- Cobots: Have lower payload and speed limitations, and require careful workflow design to avoid bottlenecks.
Automation Integration Complexity
Trends and Future Outlook
Automation is becoming more accessible across industries thanks to cobots and AI-powered programming tools:
- Rise of low-code robotics platforms
- Edge AI for adaptive behavior in cobots
- Integration of vision systems and force feedback
- Human-robot teaming for logistics, labs, and healthcare
Conclusion
While robots and cobots both enable automation, their roles differ significantly. Choosing the right solution depends on your operational scale, safety needs, and type of tasks.
- Robots are ideal for high-volume, high-speed, isolated tasks.
- Cobots are better suited for human-friendly, flexible applications.
As technologies mature, hybrid automation strategies that blend both robots and cobots are likely to dominate the smart factory landscape.